India Sets an Example with Low Gini Index in 2025
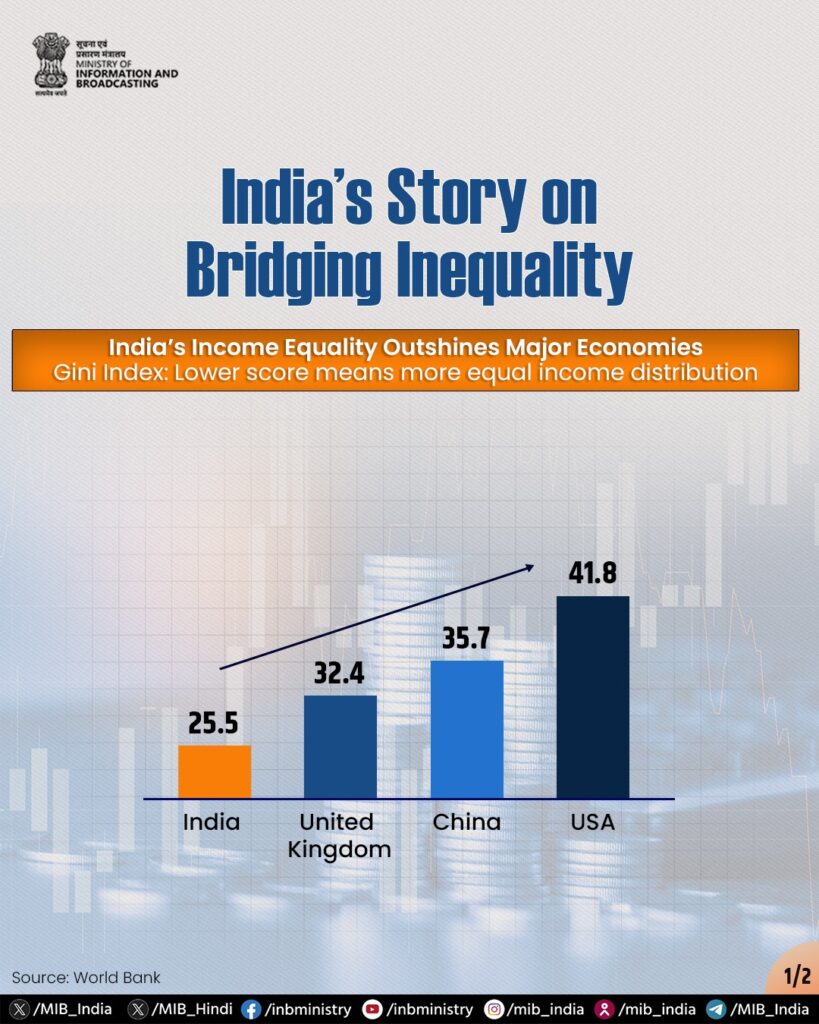
In a world where widening income inequality dominates headlines, India has charted a different course. According to the latest data, India Gini Index stands at 25.5, one of the lowest in the developing world. This index, a globally accepted measure of income distribution, signifies India’s success in reducing income inequality while continuing to grow economically.
- India Sets an Example with Low Gini Index in 2025
- What is the Gini Index and Why Is India Gini Index So Important?
- Global Context: Income Inequality vs. India’s Steady Decline in Disparity
- How India Reduced Income Inequality: Key Drivers
- 1. Food Security Through the NFSA
- 2. Universal Health Coverage via Ayushman Bharat
- 3. Employment Schemes Like MGNREGA
- Financial Inclusion: The Role of Jan Dhan and Digital India
- Education and Skilling: Bridging the Class Divide
- Rural Development and Empowerment
- Gender Equality and Social Inclusion
- Economic Growth Without Inequality: Is It Sustainable?
- Global Lessons: What the World Can Learn from India
- Expert View: Economists Laud India’s Inclusive Growth
- Conclusion: India’s Gini Index of 25.5 Is a Milestone, Not the Finish Line
This remarkable achievement isn’t accidental it reflects years of inclusive policymaking, targeted welfare schemes, and grassroots empowerment.
Key Statistic: India Gini Index at 25.5 indicates a high degree of income equality. (Lower Gini = more equal distribution)
Let’s explore how India’s focused efforts across food security, healthcare, job creation, financial inclusion, and rural development have laid a strong foundation for equitable growth.
What is the Gini Index and Why Is India Gini Index So Important?
The Gini Index, or Gini Coefficient, is a statistical measure of income or wealth inequality within a nation. It ranges from 0 (perfect equality) to 100 (extreme inequality).
A score below 30 is considered strongly equal.
India Gini Index at 25.5 in 2025 makes it a rare success among large developing economies.
This positions India as a global model for inclusive growth, especially at a time when many economies are grappling with rising inequality.
Global Context: Income Inequality vs. India’s Steady Decline in Disparity
Why is income inequality rising globally?
Many nations have seen rising income gaps due to:
- Technological disruptions
- Job polarization
- Uneven access to education and healthcare
- Declining union power
Meanwhile, India has implemented policies that actively redistribute resources and opportunities, helping reduce inequality.
📉 How does India compare globally?
| Country | Gini Index (2025) |
|---|---|
| India | 25.5 |
| Brazil | 47.9 |
| USA | 41.5 |
| China | 38.2 |
| South Africa | 63.0 |
India’s income equality outperforms even many developed nations, breaking the myth that economic growth must come at the cost of fairness.
How India Reduced Income Inequality: Key Drivers
1. Food Security Through the NFSA
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA) ensures subsidized food grains to over 75% of rural and 50% of urban populations.
- Over 810 million beneficiaries receive monthly rations.
- New AI-enabled PDS reforms reduce leakages.
Impact: Improves real income by reducing household food expenditure.
2. Universal Health Coverage via Ayushman Bharat
With Ayushman Bharat – PM-JAY, over 500 million Indians have access to free secondary and tertiary healthcare.
- Private hospitals included
- ₹5 lakh per family per year coverage
Impact: Health shocks no longer push families into poverty.
3. Employment Schemes Like MGNREGA
The MGNREGA program guarantees 100 days of wage employment to rural households.
- ₹1.3 lakh crore allocated in FY2024–25
- 260 crore person-days of employment generated
Impact: Direct transfer of income to rural poor, reducing disparities.
Financial Inclusion: The Role of Jan Dhan and Digital India
Jan Dhan Yojana and Banking Access
- Since 2014, over 52 crore Jan Dhan bank accounts have been opened.
- ₹2.07 lakh crore in deposits
- 60% accounts in rural areas
Impact: Encourages savings, enables direct benefit transfers (DBTs), and reduces informal debt dependency.
Digital Payments and UPI
- UPI transactions now exceed ₹18 lakh crore/month
- Digital wallets and mobile banking empower small vendors and rural India
Impact: Expands economic participation and reduces cash based exploitation.
Education and Skilling: Bridging the Class Divide
NEP 2020 and Skilling Programs
The National Education Policy (NEP) and programs like Skill India are building long-term human capital.
- Emphasis on foundational literacy
- 1.5 crore youth trained under Skill India
Impact: Bridges urban-rural and rich-poor education divides.
Rural Development and Empowerment
PM-Kisan and DBT Welfare Programs
- Over ₹2.8 lakh crore has been transferred directly to farmers under PM-Kisan since launch.
- ₹6,000 per year per farmer household
- Instant credit to bank accounts via DBT
Impact: Reduces dependence on exploitative credit and empowers rural income earners.
Gender Equality and Social Inclusion
Women-Led SHGs and Stand-Up India
- Over 81 lakh SHGs (Self-Help Groups) active nationwide
- Stand-Up India scheme facilitates women and SC/ST entrepreneurs
Impact: Empowers women financially, narrowing gendered income gaps.
Economic Growth Without Inequality: Is It Sustainable?
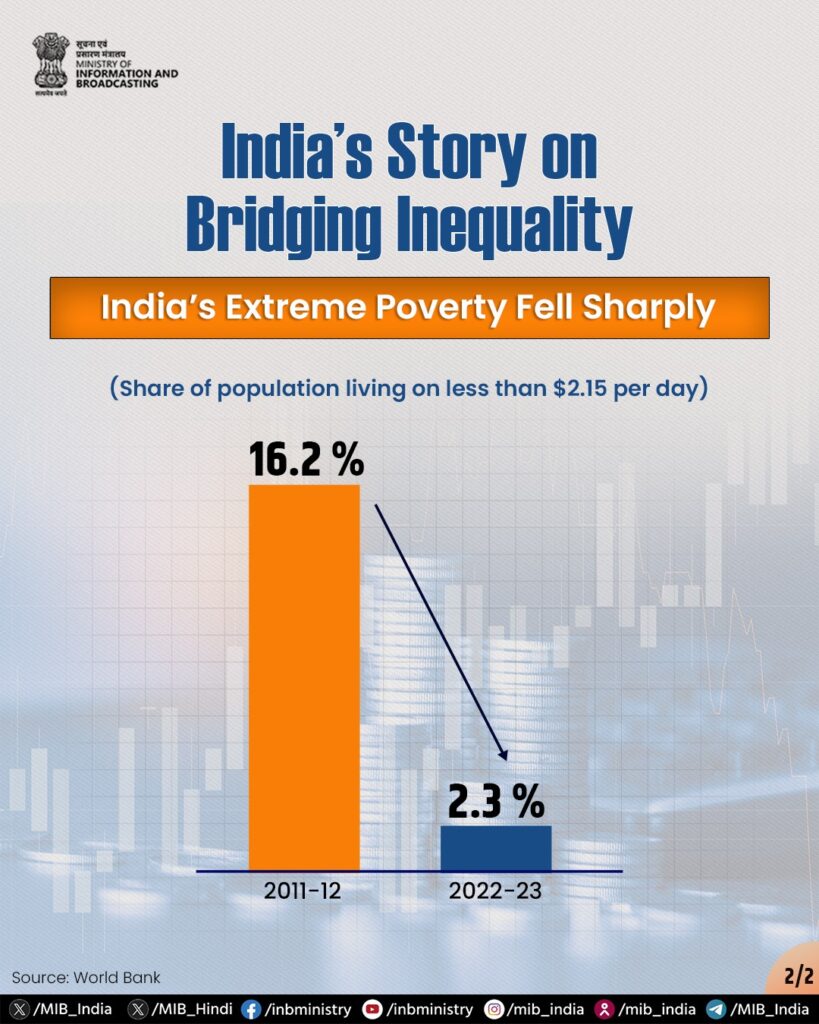
India’s Gini Index of 25.5 proves that economic growth and income equality can co-exist when backed by policy intent.
Future Challenges:
- Urban income gaps
- Underemployment in certain sectors
- Climate linked agricultural stress
India must continue investing in health, education, infrastructure, and green jobs to sustain its equality success.
Source: World Bank & MI&B
Global Lessons: What the World Can Learn from India
India’s model offers actionable lessons:
- Universal food access and DBTs reduce economic vulnerability
- Digital financial infrastructure ensures transparency
- Community led models (like SHGs and Gram Panchayats) enable local resilience
As inequality becomes a global election issue, India’s Gini Index milestone is a wake up call for inclusive capitalism.
Expert View: Economists Laud India’s Inclusive Growth
Dr. Ramesh Chand (NITI Aayog member): “India’s focus on real income redistribution not just GDP is why its Gini Index is globally admired.”
Jean Dreze, development economist: “India’s welfare architecture, while imperfect, is still among the most ambitious and inclusive in the world.”
Pic Credits: World Bank and MI&B (Only for graphical representations)
Conclusion: India’s Gini Index of 25.5 Is a Milestone, Not the Finish Line
India has proved that growth doesn’t need to be unequal. With a Gini Index of 25.5, it has shown the world how targeted policies, digital inclusion, and people-first development can transform lives and bridge class divides.
But the road ahead needs:
- Continued focus on informal workers
- Urban poor upliftment
- Sustainable green employment
The world is watching India not just as an economic powerhouse, but as a beacon of equitable development.
Stay Connected with The News Drill for more updates.
Have a tip, story, or insight about India’s growth story? Email us at editor@thenewsdrill.com or visit our contributor page.
Contact us: contact@thenewsdrill.com