Government Spending on Freebies in India (2024–25)
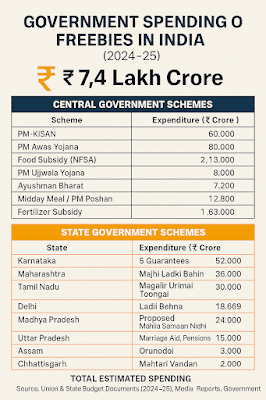
💸Estimated total expenditure: ₹7.4 Lakh Crore
Central Government Schemes:
| Scheme | Expenditure (₹ Crore) |
|---|---|
| PM-KISAN | 60,000 |
| PM Awas Yojana | 80,000 |
| Food Subsidy (NFSA) | 2,13,000 |
| PM Ujjwala Yojana | 8,000 |
| Ayushman Bharat | 7,200 |
| Midday Meal / PM Poshan | 12,800 |
| Fertilizer Subsidy | 1,63,000 |
State Government Schemes:
| State | Scheme | Expenditure (₹ Crore) |
|---|---|---|
| Karnataka | 5 Guarantees | 52,000 |
| Maharashtra | Majhi Ladki Bahin | 36,000 |
| Tamil Nadu | Magalir Urimai Thogai | 30,000 |
| Delhi | Free Electricity, Transport | 10,000 |
| Madhya Pradesh | Ladli Behna | 18,669 |
| Bihar | Proposed Mahila Samaan Nidhi | 24,000 |
| Uttar Pradesh | Marriage Aid, Pensions | 15,000 |
| Assam | Orunodoi | 3,000 |
| Chhattisgarh | Mahtari Vandan | 2,000 |
Total Estimated Spending
- Central Government: ₹5.44 Lakh Crore
- State Governments: ₹2.00 Lakh Crore
- Combined: ₹7.4 Lakh Crore
Source: Union & State Budget Documents (2024–25), Media Reports, Government Portals.
The Cost of Freebies: Impact on India’s Economy
Freebies, while intended to provide immediate relief, can have long-term implications on a state’s fiscal health and economic development. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has cautioned that such expenditures may crowd out essential investments in social and economic infrastructure.
💸 Freebies: A Termite Eating Away at India’s Economy
Key Highlights:
RBI’s Warning: Freebies like farm loan waivers and free electricity could divert resources from essential infrastructure development.
State Expenditures: States like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh have significantly increased budgets for welfare schemes.
Fiscal Implications: Excessive spending on freebies can lead to higher fiscal deficits and reduced
capital expenditure.
India’s landscape of welfare schemes, often termed “freebies,” varies across states, encompassing initiatives in education, healthcare, agriculture, and social welfare. Here’s an overview of notable schemes from different states:
🟩 Uttar Pradesh
OBC Marriage Aid Scheme: Provides ₹20,000 to OBC girls at marriage. Beneficiaries increased from 55,551 in 2023–24 to 1 lakh in 2024–25.
Divyangjan Pension Scheme: Disbursed ₹1,300 crore to 11.04 lakh beneficiaries.
Free Bus Travel: Over 31 lakh beneficiaries enjoy free bus travel.
🟨 Karnataka
Shakti Scheme: Empowers women with free bus travel.
Anna Bhagya: Provides free rice to BPL families.
Gruha Jyoti: Offers 200 units of free electricity to households.
Yuva Nidhi: Financial aid for unemployed graduates and diploma holders.
Gruha Lakshmi: Monthly assistance to women homemakers.
These five guarantees have positively impacted 70 million residents.
🟦 Odisha
Subhadra Yojana: Launched in September 2024, this scheme provides direct financial assistance to women aged 21 to 60, aiming to benefit over 1 crore women across the state.
🟥 Rajasthan
Indira Rasoi: Offers subsidized meals at ₹8, with the state subsidizing ₹17 per meal.
🟧 Madhya Pradesh
Health Insurance for State Employees: Extends health insurance coverage to all state government staff.
🟪 Uttarakhand
e-RUPI System: A digital payment system for transparent subsidy distribution to farmers.
🟫 Central Government Schemes
PM-KISAN: Provides ₹6,000 annually to eligible farmers.
PM Ujjwala Yojana: Offers free LPG connections to BPL families.
Ayushman Bharat: Health insurance coverage up to ₹5 lakh per family per year.
PM Awas Yojana: Affordable housing for urban and rural poor.
PM Poshan: Mid-day meal scheme for school children.
For a comprehensive list of central and state government schemes, you can refer to the National Portal of India and Open Budgets India.
🟩 Madhya Pradesh: Ladli Behna Yojana
Monthly Assistance: ₹1,250 to married women aged 21–60.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): ₹18,669 crore.
Beneficiaries: Approximately 1.27 crore women.
Total Disbursed So Far: Over ₹28,000 crore.
Additional Transfers: ₹341 crore for 56.83 lakh social security pensioners and ₹30.83 crore for LPG cylinder refills for over 26 lakh women.
🟨 Delhi: Mahila Samridhi Yojana
Monthly Assistance: ₹2,500 to eligible women.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): ₹5,100 crore.
Eligibility: Women aged 18–60 with annual income up to ₹2.5 lakh.
🟥 Maharashtra: Mukhyamantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana
Monthly Assistance: ₹1,500 to women.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): ₹36,000 crore.
Total Disbursed So Far: ₹33,232 crore.
Beneficiaries: Approximately 2.5 crore women.
🟦 Chhattisgarh: Mahtari Vandan Yojana
Monthly Assistance: ₹1,000 to women.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): Data not specified.
🟧 Tamil Nadu: Magalir Urimai Thogai
Monthly Assistance: ₹1,000 to women.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): Data not specified.
🟪 Assam: Orunodoi Scheme
Monthly Assistance: ₹1,250 to women.
Total Budget Allocation (FY25–26): Data not specified.
🟫 Bihar: Proposed Mahila Samaan Nidhi
Proposed Monthly Assistance: ₹2,500 to women from underprivileged communities.
Status: Announced as an election promise by the Mahagathbandhan alliance; implementation pending election results.
🟥 Karnataka: Gruha Lakshmi Scheme
Monthly Assistance: ₹2,000 to women heads of households.
Total Budget Allocation (FY24–25): ₹28,608 crore.
Beneficiaries: Approximately 1.1 crore women.
💰 Cumulative Expenditure on Women’s Cash Transfer Schemes
Across various states, the cumulative expenditure on women’s cash transfer schemes for FY25–26 is substantial:
Madhya Pradesh: ₹18,669 crore.
Delhi: ₹5,100 crore.
Maharashtra: ₹36,000 crore.
Karnataka: ₹28,608 crore.
These figures highlight the significant financial commitments made by state governments towards welfare schemes aimed at women’s empowerment.
Note: While these schemes aim to provide immediate relief and support to women, concerns have been raised about their long-term fiscal sustainability. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has cautioned that such expenditures may crowd out essential investments in social and economic infrastructure.